*Corresponding Author:
Papadopoulos Iordanis,
Department of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics and ex. Department of Aesthetic and Cosmetology, International Hellenic University, Thessaloniki, Greece
E-mail: driordanis@yahoo.gr
Abstract
Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease is a systemic rheumatic disease with various clinical and laboratory findings that does not meet the criteria for its classification. It affects 25% of rheumatic patients and is usually manifested by Raynaud’s phenomenon, inflammatory polyarthritis, non-specific rash and interstitial lung disease. There is usually no renal involvement. We present a male patient with arthralgia, fever, hematuria and erythema annulare centrifugum with ear nodules. The symptoms subsided after two months and a year later the patient continues to have no symptoms and takes 1mg methylprednisolone daily. The simultaneous presence of these two dermatological findings has not been reported again in the context of Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease.
Keywords
Centrifugum; Dermatology; Ear nodules; Erythema annulare; Lupus erythmatoses; Rheumatology; Undifferentiated connective tissue disease
Introduction
The term of Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease was first formulated thirty years ago and has replaced the term latent lupus. It is a systemic rheumatic disease with various clinical and laboratory findings that does not meet the criteria for its classification [1]. It affects 25% of rheumatic patients and is usually manifested by Raynaud’s phenomenon, inflammatory polyarthritis, non-specific rash and interstitial lung disease. There is usually no renal involvement. Findings of the disease include evidence of systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, myositis and vasculitis. Eventually, within 5 years, 30% of patients are diagnosed with a specific rheumatic disease [2].
Erythema annulare centrifugum occurs in various diseases such as fungal infections (tinea corporis), Lyme disease, Pityriasis rosea, secondary syphilis and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematoses [3]. The duration of the rash depends on the cause. Sometimes it is slightly itchy.
Nodules in the ear helix have been observed in various rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis [4]. Also chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis has been reported on Raynaud’s syndrome [5].
The most common dermatological manifestation of Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease is Raynaud’s phenomenon [6].
The simultaneous presence of erythema annulare centrifugum and ear nodules has not been reported again in the context of Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease.
Case Report
A 46-year-old man was examinated in September 2020 with an erythema annulare centrifugum with a mild itching (Figure 1). He reported low grade fever for a month and occasional arthralgia of the ankle and elbow joints as well as fasciculations in the proximal limb muscles. The skin lesion remains for 10 days without topical treatment. The blood exams shows E.S.R. 57, ANA 1/5.120, C3 95mg/ dl, CRP 19,73 mg/dl, RF negative, Vitamin D 18,56ng/dl, Ht 39%, anti-ds DNA 234 U/ml, 10-12 red blood cells in the urine test without white blood cells and without proteinouria.
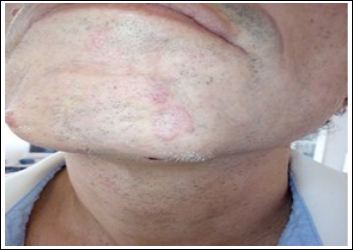
Figure 1: UCTD Erythema annulare centrifugum.
He was prescribed hydroxychloroquine 200mg twice per day. After 4 days he had fever 38.5⁰C, fatique, malaise, dyspnea and acute chest pain (pericarditis). He started methylprednisolone 32mg per day and he had clinical improvement. Methylprednisolone was gradually reduced according to the clinical presentation and the finding of the red blood cells in the urine test. A month later he developed ear nodules which remained for a week (Figure 2). One year later he has no clinical signs. The blood exams are normal except ANA 1/1280. The only medication he takes is methylprednisolone 1mg and oral vitamin D 4.000 units three times per week.

Figure 2: UCTD Ear nodules.
Discussion
The Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease is a common rheumatological situation with uncommon dermatological manifestations from different rheumatological diseases. The ear helix nodules and the erythema annulare centrifugum haven’t been reported to appear simultaneously at the same patient. The patient took the m-RNA vaccine for COVID-19 and 6 weeks later, gets COVID-19 infection without any specific clinical finding. It is worth mentioning that both vaccination and disease did not trigger a relapse of the rheumatologic disease.
Patients with Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease show vitamin D deficiency [7]. Perhaps there is a role for the vitamin D for the Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease and COVID-19 disease [8].
References
- Pepmueller PH (2016) Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease, Mixed Connective Tissue Disease, and Overlap Syndromes in Mo Med 113: 136-140.
- Bodolay E, Szegedi G (2009) Undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Orv Hetil 150: 867-872.
- Trayes K, Savage K, Studdiford J (2018) Annular Lesions: Diagnosis and Am Fam Physician 98: 283-291.
- Chabra I, Singh R (2013) Gouty tophi on the ear: A Cutis 92: 190-192.
- Giraldo W, González-García C, Alonso E, Bujidos C (2014) Chondrodermatitis nodularis chronica helicis in a patient with systemic sclerosis associated with primary biliary cirrhosis (Reynolds syndrome): A case report. Eur J Rheumatol 1: 161-163.
- Sen S, Sinhamahapatra P, Choudhury S, Gangopadhyay A, Bala S, et al. (2014) Cutaneous Manifestations of Mixed Connective Tissue Disease: Study from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Eastern India. Indian J Dermatol 59: 35-40.
- Cutolo M (2008) Vitamin D or hormone D deficiency in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, including undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res Ther 10: 123.
- Mercola J, Grant W, Wagner C (2020) Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity. Nutrients 12: 3361.
Citation: Papadopoulos I (2021) Undifferentiated Connective Tissue Disease with Unusual Dermatological Findings. Case Report. J Clinic Exper Cosme Derma 4: 019.
Copyright: © 2021 Papadopoulos I. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.


