*Corresponding Author:
Houria Sahel,
Department of dermatology, CHU, Bab El Oued, Algiers Algeria
Tel: +213 777000672
E-mail: houriasahel2015@gmail.com
Keywords
Erythrodermic psoriasis; Etanercept, Infliximab
Background
Classical treatment options for Erythrodermic Psoriasis (EP) are limited and occasionally associated with toxicity. The safety and effica- cy of biological therapies have been demonstrated in psoriatic arthri- tis and moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. We report the efficacy of etanercept and infliximab in EP in two cases.
Observations
Case 1: A male patient 30 years old, has psoriasis since he has 17 years old. He received phototérapy, retinoid and ciclosporin without improvement. Methotrexate causes an improvement but stopped it because of a digestive intolerance.
In the last two months, he has a dry desquamative EP (PASI: 32.8) with arthritis of both ankles. Laboratory test before biologic treatment were normal. He received subcutaneous injection of etanercept 50mg × 2 / week. At week 12, a clinical improvement in the patient condition was observed. Erythematic, scaling and itching showed a rapid response, with significantly reducing the PASI score to 7 (Figure 1).
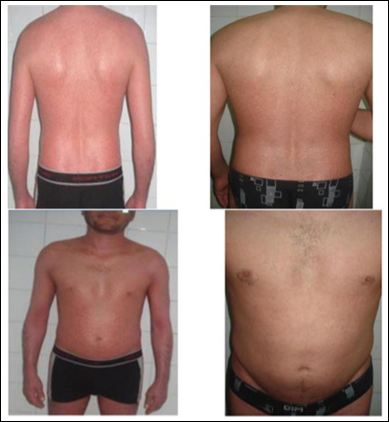
Figure 1: (Frontal picture) and (Back picture).
Case 1: Before (right) and after (left) 12 weeks of « etanercept » treatment.
Case 2: Before (right) and after (left) 12 weeks of « etanercept » treatment.
Case 2: A male patient 45 years old, with a history of colitis ulcerosa, an idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and a primary sclerosing cholangitis. He has psoriasis since he was 26 years old. He received methotrexate, retinoid, and phototherapy without improvement. In the last 4 months, he developed a dry desquamative EP (PASI:37) with arthritis of both knees. Laboratory test before biologic treatment were normal except for thrombocytopenia: 109,000 / mm3. He received intravenous infusion of infliximab at a dose of 5mg / kg. At the third infusion, a significant improvement of EP was noted (PASI: 4,8) with a remission of arthritis (Figure 2).
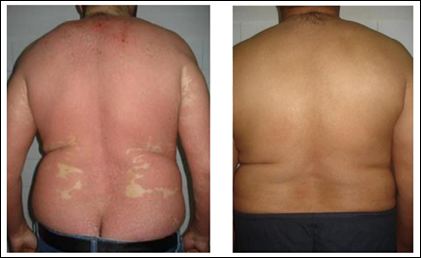
Figure 2: Case 2: Before (right) and after (left) 6 weeks of « infliximab » treatment.
In both cases, standard laboratory tests, including hematological evaluations, serum biochemistry and urinalysis profiles, were performed every 4 weeks. No adverse effects were observed during treatment. In particular, no cases of injection site reaction, severe respiratory infection or drug related laboratory abnormalities occurred. Patients are continuing treatment.
Discussion
EP is a severe and disabling variant of psoriasis. The management of EP can be unsatisfactory with older conventional therapies, such as UVB-NB, ciclosporin, methotrexate and retinoid.
Etanercept and infliximab have been approved for the control of psoriatic arthritis and moderate to severe plaque psoriasis but not for EP. A case series of ten patients demonstrates that etanercept is a highly effective treatment for EP, that provides rapid and significant clinical response associated with an excellent safety profile [1]. Infliximab is the most frequently used biological agent in the treatment of EP, with a total of 53 cases reported [2]. However, it appears critical to address the respective tolerance profiles and the risk ⁄benefit ratio of different biologic treatments in patients with EP. A severe hypoglycemia after initiation of anti tumor necrosis factor therapy with etanercept was reported in a patient with generalized pustular psoriasis and type 2 diabetes mellitus [3]. A multicentre national retrospective study was performed using the French Psoriasis Group network [4]. Patients showing psoriasis involving at least 90% of body surface area (BSA), and in whom severity of the disease had been evaluated before and after 3 and ⁄or 6 months of treatment with biologics, were enrolled in the study. 28 patients were included, representing 42 flares of erythrodermic psoriasis treated with infliximab (n = 24), adalimumab (n = 7), etanercept (n = 6), ustekinumab (n = 3) or efalizumab (n = 2). A 75% improvement of BSA or PASI 12-14 weeks after treatment onset was reached in 48% of flares treated with infliximab, in 50% of those treated with adalimumab and in 40% of those treated with etanercept. Twelve serious adverse events, consisting of bacterial infection in seven of them, were observed. Biological treatment was discontinued for safety concern in 19% of cases. A given biologic was administered for up to 48 weeks in 34% of flares. So biologics show overall good short term efficacy, but treatment switch due to lack of efficacy or side effects was frequently observed on a longer term.
As skin inflammation is the predominant feature in EP, a rapid systemic release of TNF-α may be responsible for the disease onset and severity. Consequently, the administration of TNF-α blocking agent, leading to a rapid neutralization of this cytokine, could explain their significant and rapid effect in our cases.
Conclusion
In our two cases, the rapidity of clearance and the excellent safety profile suggest a role of etanercept and infliximab in the management of EP that is unresponsive to conventional treatment. These results should be confirmed by more studies.
References
- Esposito M, Mazzotta A, de Felice C, Papoutsaki M, Chimenti S (2006) Treatment of erythrodermic psoriasis with etanercept. Br J Dermatol 155: 156-159.
- Stinco G, Errichetti E (2015) Erythrodermic psoriasis: current and future role of biologicals. BioDrugs 29: 91-101.
- Wambier CG, Foss-Freitas MC, Paschoal RS, Tomazini MV, Simão JC et Severe hypoglycemia after initiation of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy with etanercept in a patient with generalized pustular psoriasis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Acad Dermatol 60: 883-885.
- Viguier M, Pagès C, Aubin F, Delaporte E, Descamps V, et (2012) Efficacy and safety of biologics in erythrodermic psoriasis: a multicentre, retrospective study. Br J Dermatol 167: 417-423.
Citation: Sahel H, Bouadjar B (2017) Treatment of Erythrodermic Psoriasis with Infliximab and Etanercept in Two Cases. J Clinic Exper Cosme Derma 1: 002.
Copyright: © 2017 Sahel H. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.


